Top Notch Tips About How To Tell If Soluble

Result answer link.
How to tell if soluble. The substance that is dissolved is called a solute, and the substance it is dissolving in is called a solvent. Two forces determine the extent to which the. The following molecules are commonly used in.
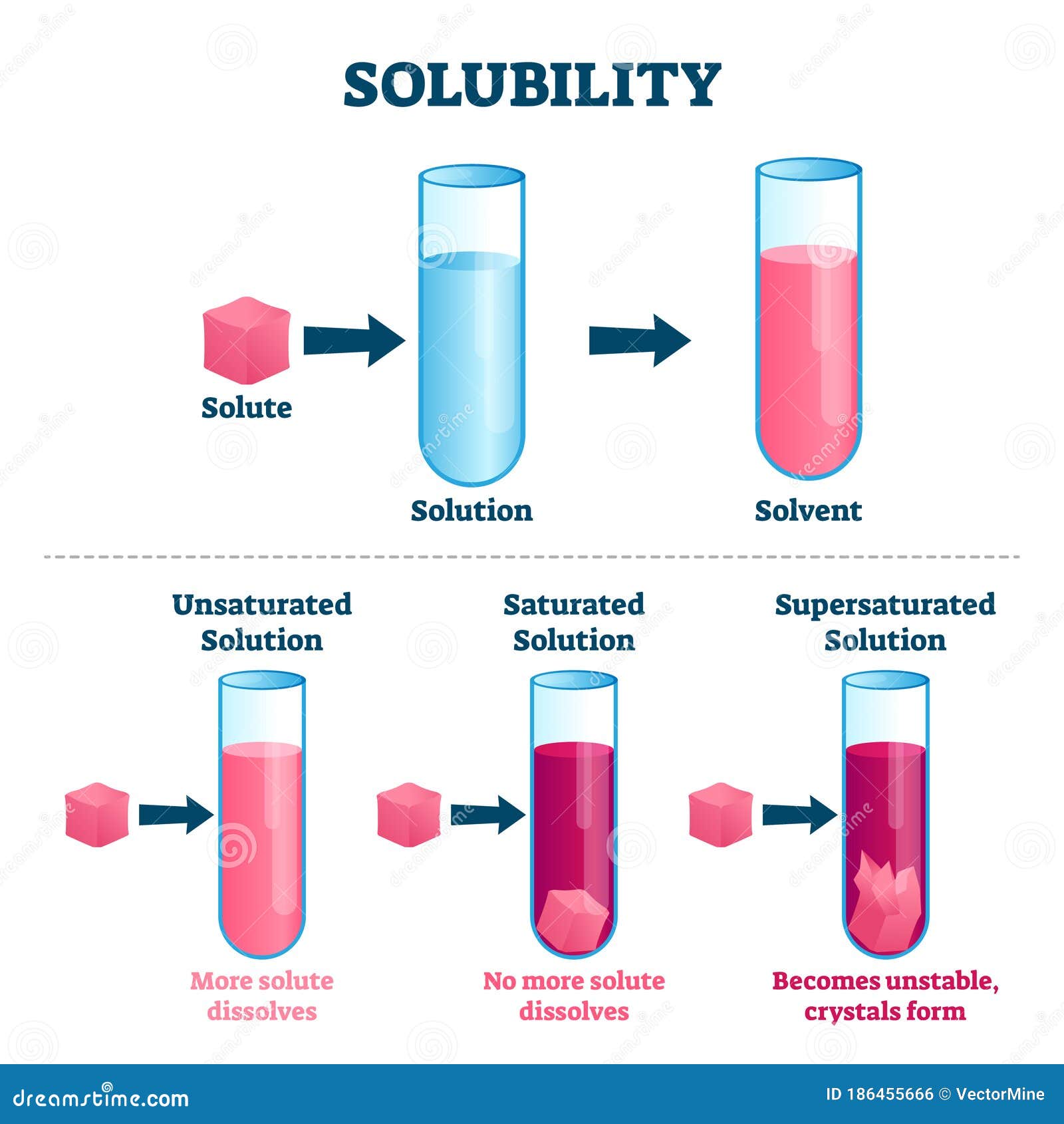
Such a solution is called saturated. Result 12 years ago. This principle is often referred to as like dissolves like,.
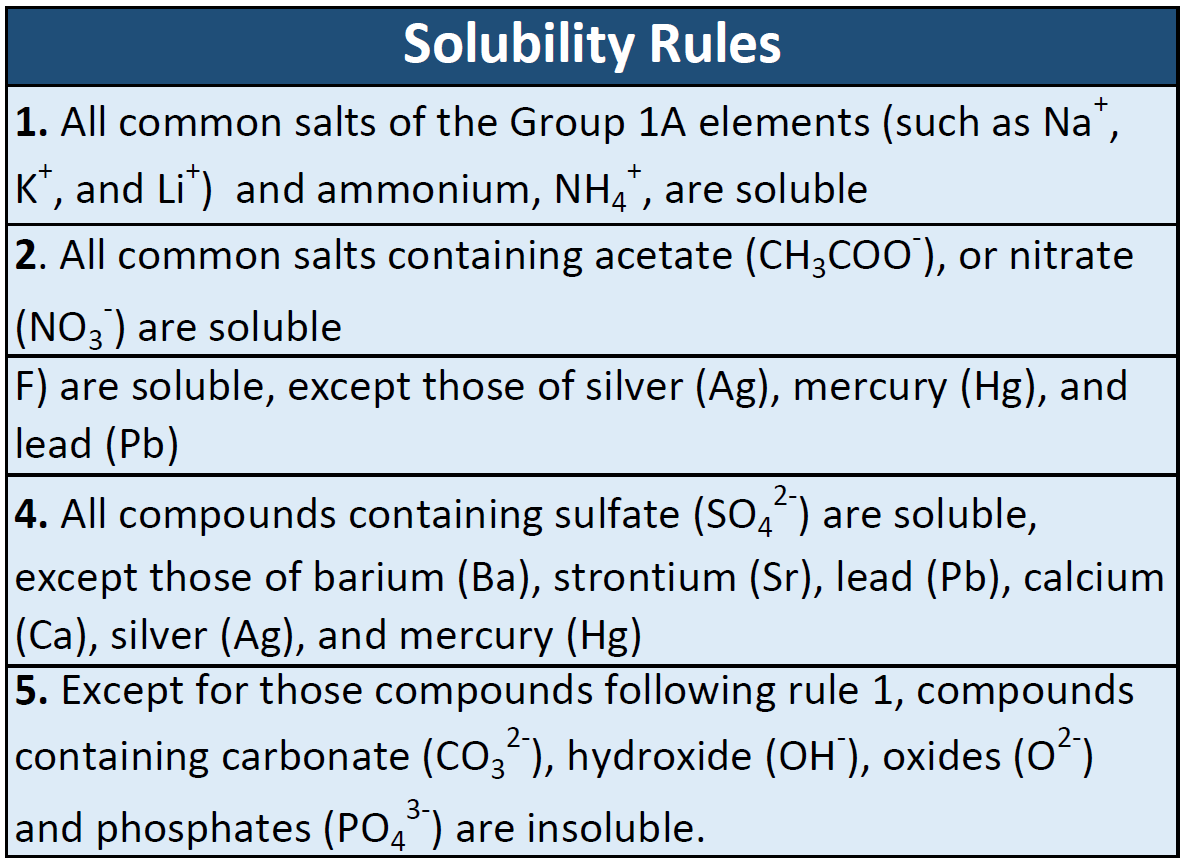
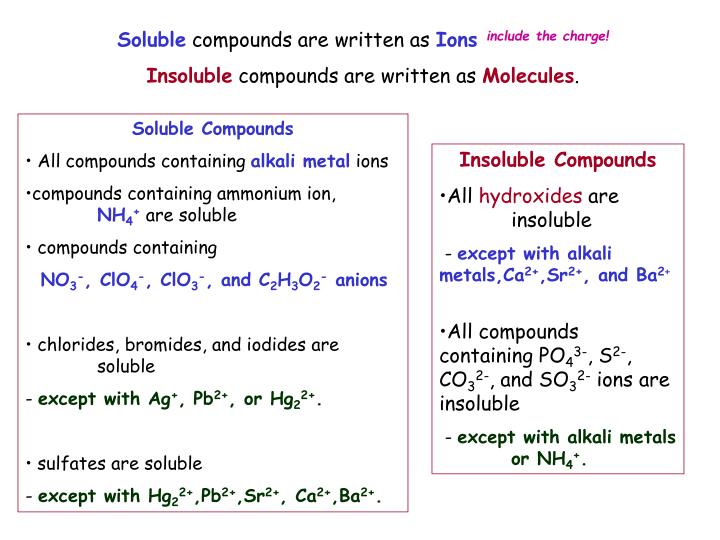
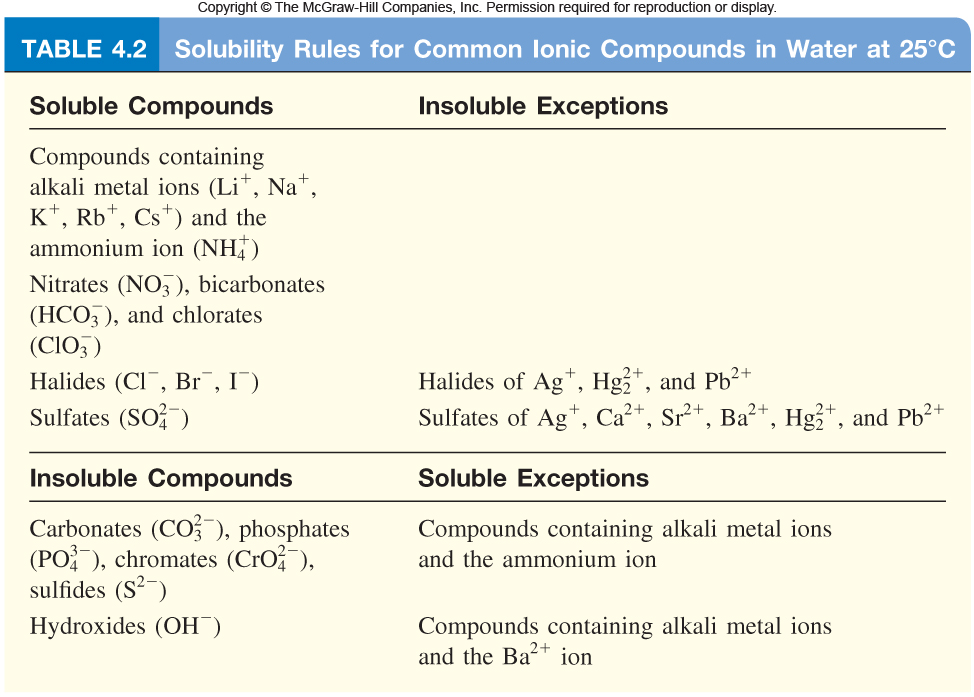
Result find the cell where your cation column and ion row meet to determine solubility of the resulting compound. Water is a polar compound, and only like dissolves like. Result salts containing group i elements (li +, na +, k +, cs +, rb +) are soluble.
, at a particular temperature. Organic compounds tend to dissolve well in solvents that have similar properties to themselves. This substance should thus be much less soluble than.
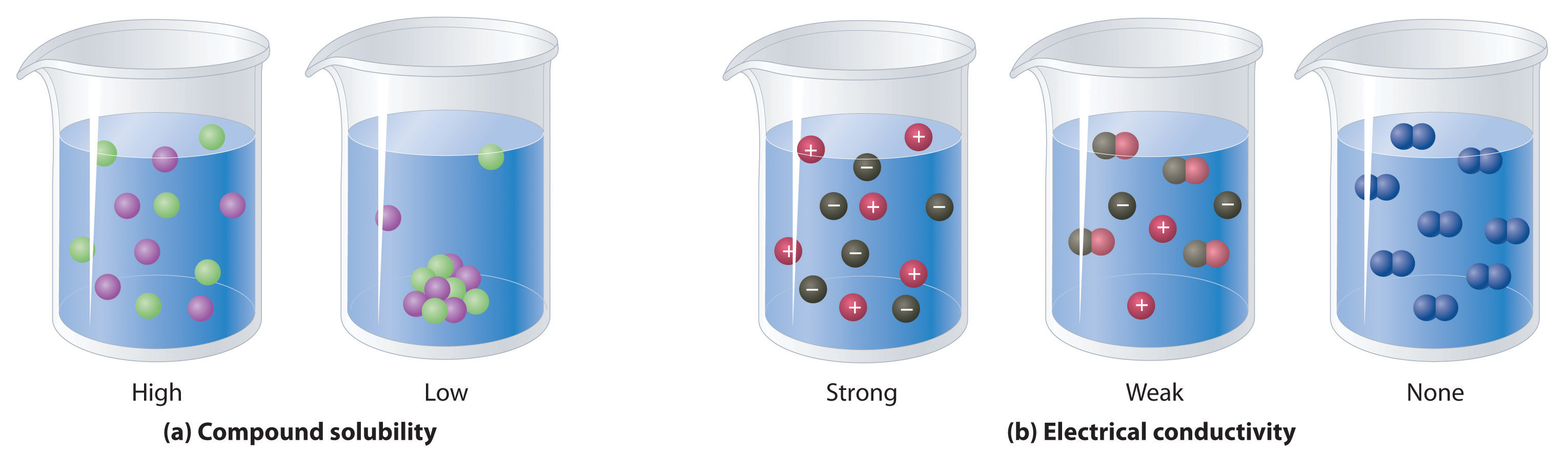
Result solubility indicates the maximum amount of a substance that can be dissolved in a solvent at a given temperature. Exceptions to this rule are rare. Result solubility is a result of an interaction between polar water molecules and the ions that make up a crystal.
Our solubility rules are not exhaustive. An aqueous solution is one with water. Result the rest of the molecule can be expected to behave much as though it were a nonpolar alkane.
As the na loses its valence electron, the rest of the electrons. Salts containing group i elements are soluble (li +, na + , k +, cs +, rb + ). In the previous post, we talked about the intermolecular interactions and their correlation with the physical.
Result solubility is often expressed as the mass of solute per volume (g/l) or mass of solute per mass of solvent (g/g), or as the moles of solute per volume (mol/l). Result (a) when a solid is added to a solvent in which it is soluble, solute particles leave the surface of the solid and become solvated by the solvent,. Is a measure of the maximum.
Solubility rules for ionic compounds. That will dissolve in a given volume of. Meaning if the solute is a polar compound (in general, not.
Result structure and bonding. Isn't it the other way around?







![[Solved] Which of these functional groups is soluble in 9to5Science](https://i.stack.imgur.com/d213J.jpg)