Underrated Ideas Of Tips About How To Obtain Embryonic Stem Cells
Single cells taken from the blastula are grown into.
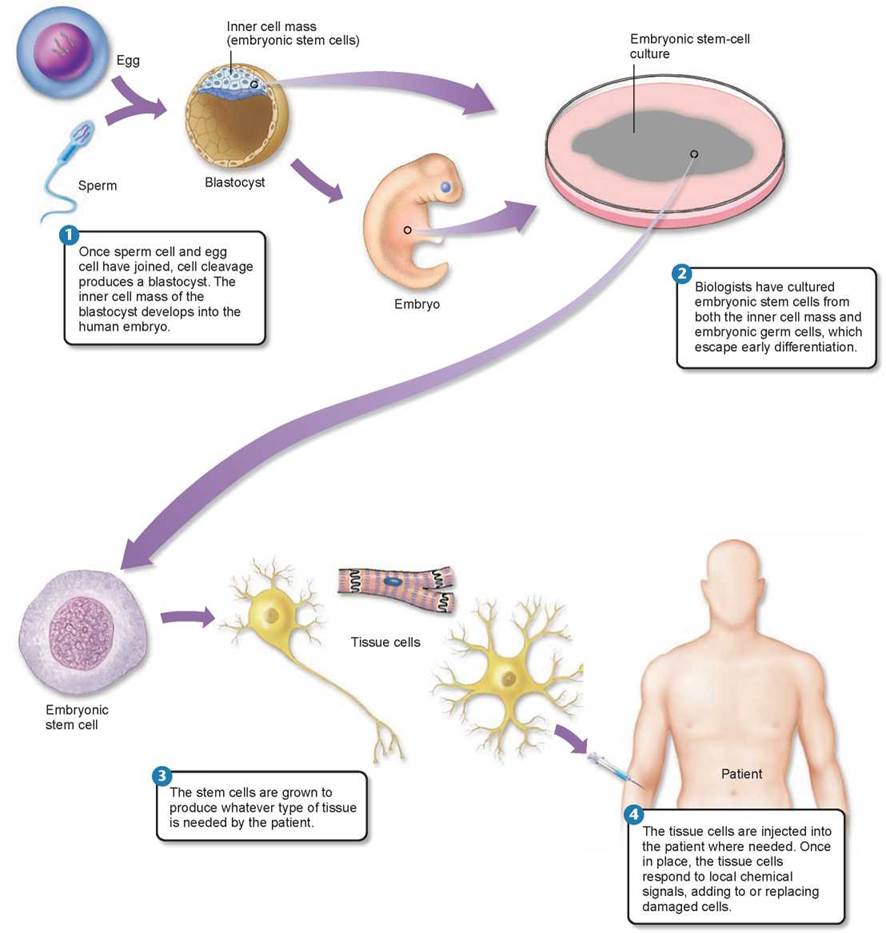
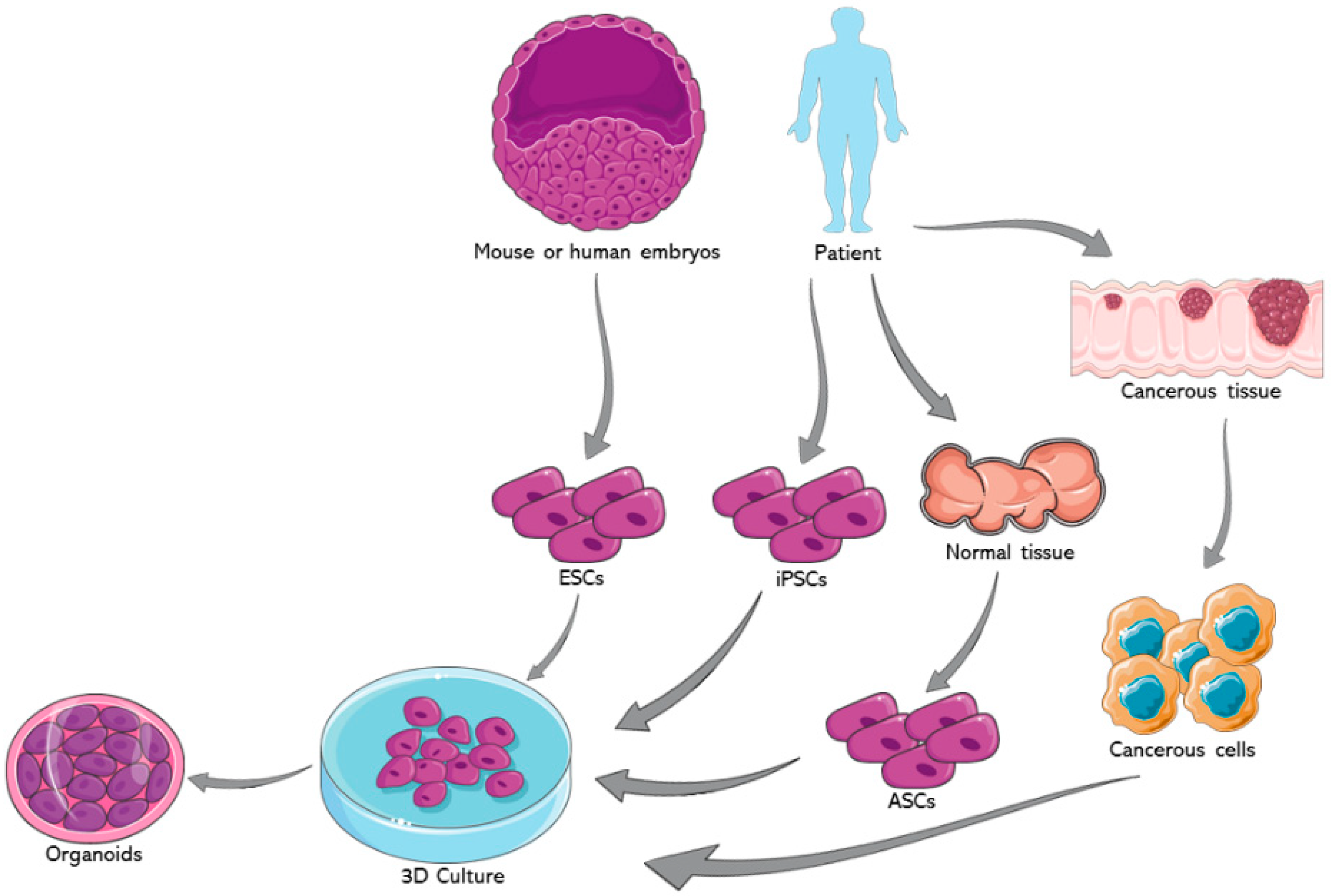
How to obtain embryonic stem cells. Embryonic stem cells of the inner cell mass are pluripotent, meaning they are able to differentiate to generate primitive ectoderm, which ultimately differentiates during. The building blocks of synthetic embryos. Human embryonic stem cells (hes) were initially derived in 1998 1 and have enormous potential as a source of cells for cell replacement therapies and as.
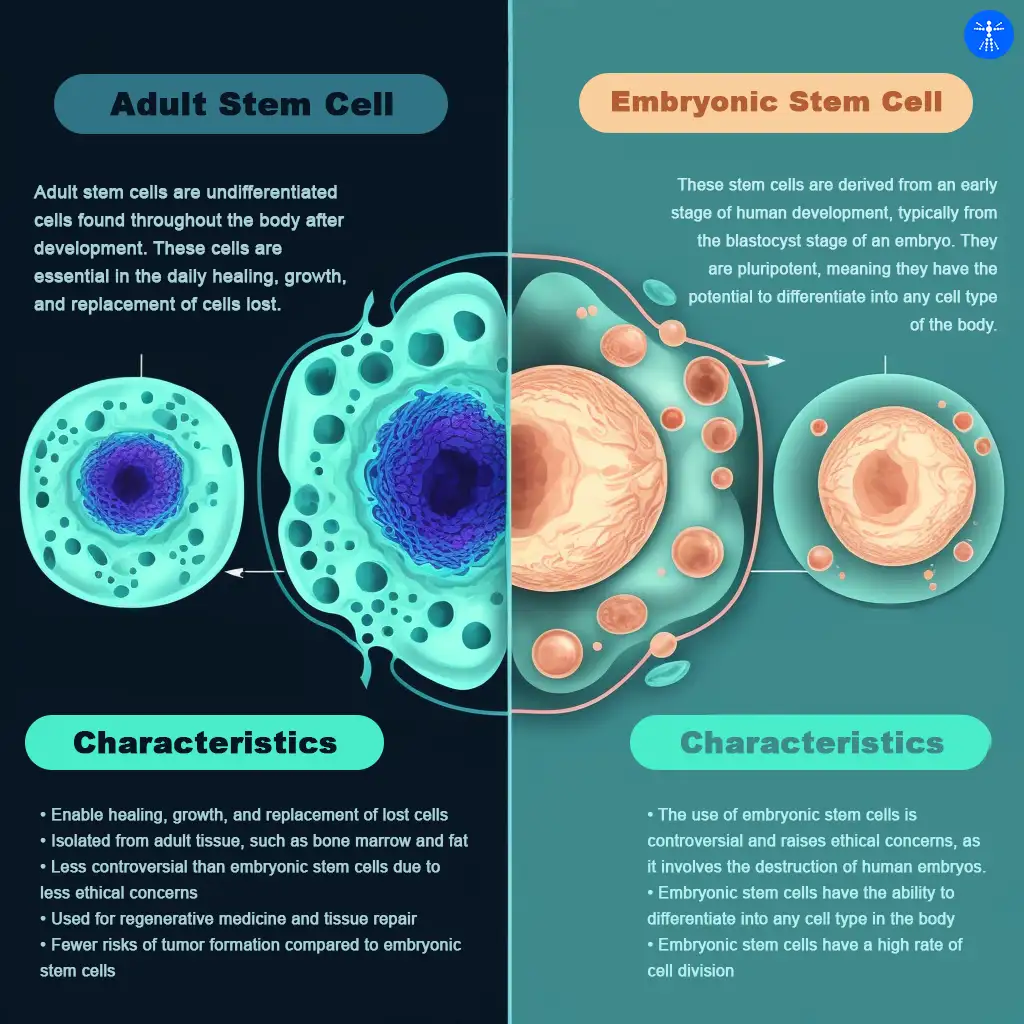
Stem cells are the body's raw materials — cells from which all other cells with specialized functions are. Embryonic stem cells (escs): Embryonic stem cells are usually derived from the primitive (undifferentiated) cells of the inner cell mass, which have the potential to become a wide variety of specialized cell.
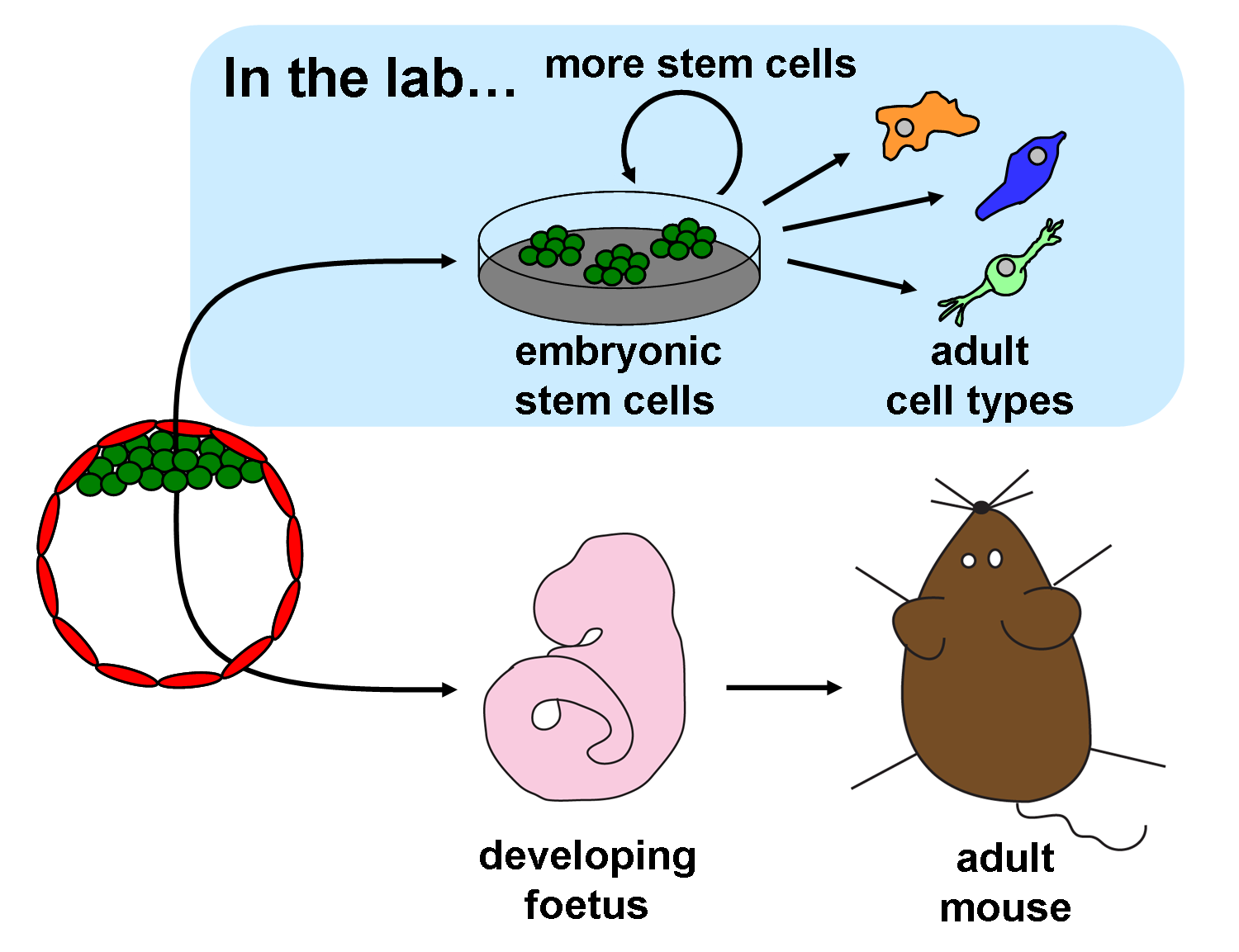
Embryonic stem cells have huge potential in the field of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine as they hold the capacity to produce every. Human embryonic stem cells (escs) are created from a small number of cells found in a blastula, a very early human embryo. This pioneering model, also called a gastruloid, captured key aspects of early human.
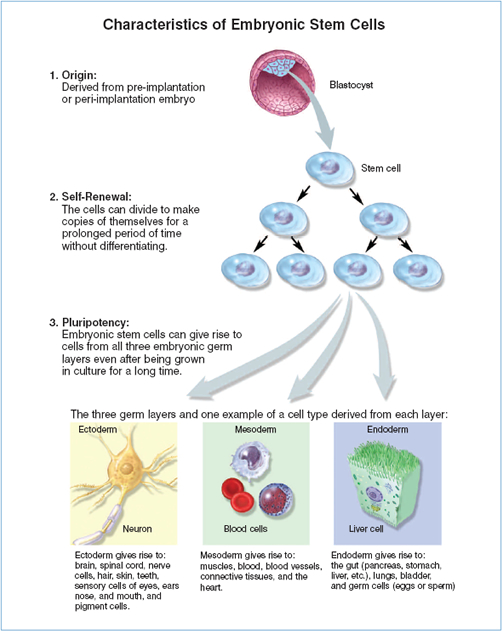
Embryonic stem (es) cells are characterized by the qualities of pluripotence, the ability to give rise to cell types representative of all the tissues of the. Once an egg cell is fertilized by a sperm, it will divide. Embryonic stem cells (esc) are pluripotent cells which give rise to all somatic cell types in the embryo.
Researchers created the first human embryo model from embryonic stem cells in 2014. The rest is just growth. Stephanie watson & craig freudenrich, ph.d.
Skin stem cells are found in the basal layer of the epidermis and form keratinocytes for the continuous regeneration of the epidermal. Esc can be a valuable tool for. Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent cells isolated from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, the early mammalian embryo that implants into the uterus.
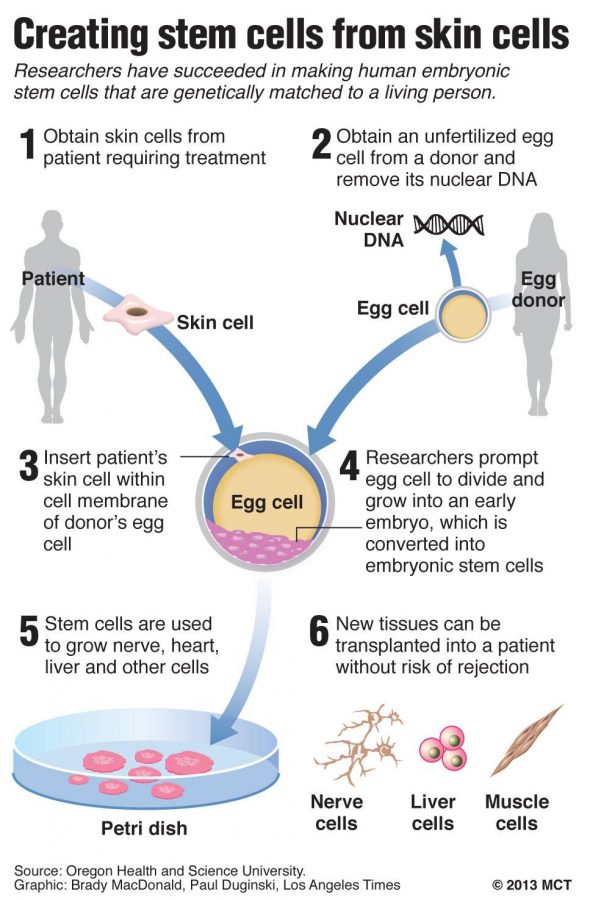
Induced pluripotent stem cells (ipscs) are reprogrammed somatic cells that possess the unique ability to revert to a pluripotent state, enabling. Skin stem cells. Embryonic stem cells (escs) are found in the inner cell mass of the human blastocyst, an early stage of the developing embryo lasting from the 4th to 7th day after fertilization.
Embryonic stem cells have achieved prominence in part because of the still unsubstantiated hopes that therapies that use them can ameliorate a variety of human. The cells of a blastocyst are totipotent, meaning that they have the ability to differentiate into any cell type in the body. The human bone marrow niche consists of a variety of vascular and mesenchymal cells that regulate and support blood cell production throughout life, but.
Are made from embryonic stem cells which can develop into any cell type. The first four weeks of human embryo development is when the embryo makes all of its organs. During this period it’s just impossible to obtain samples.
An embryonic stem cell is a cell derived from the early stages of an embryo which is capable of differentiating into any type of body cell.